Endometrial tumors are divided into benign and malignant.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that make up the endometrium. There are other, less common types of cancer that can form in the uterus, including uterine sarcoma.
Fortunately, uterine cancer is detected at an early stage. This is because it often expresses itself early with vaginal bleeding and often a hysterectomy is the treatment. Other symptoms include bleeding between periods or pelvic pain.
A genetic mutation transforms the normal cells that line the uterus into abnormal cells that . It grows and multiplies at an uncontrollable rate and leads to a tumor. Then it invades nearby tissues, and then it can move to distant places in the body if diagnosis and treatment is delayed..
There are many factors that increase the risk of developing uterine cancer, including:
- Fluctuations in the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones.
- Starting menstruation at an early age – before 12 y and or cessation at a later age increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Not being pregnant increases the risk compared to being pregnant even once.
- Aging, as most cases occur after menopause
- weight and obesity cause hormonal imbalance
- hereditary Lynch syndrome It is a syndrome that increases the risk of colon, uterine , and other cancers
- Tamoxifen is used as a hormonal treatment for breast cancer
To reduce the risk of endometrial cancer:
- Recognize the risks of hormone therapy to control menopausal symptoms .
- Taking oral contraceptives for at least one year may reduce The possibility of uterine cancer.
- Exercising and maintaining an ideal weight.
To diagnose uterine cancer, the patient undergoes:
- Clinical examination.
- Pelvic or transvaginal US to detect the thickness and texture of the endometrial wall and help to rule out other conditions.
- DC and biopsy
- CT
- MRI
- PET CT
Treatment:
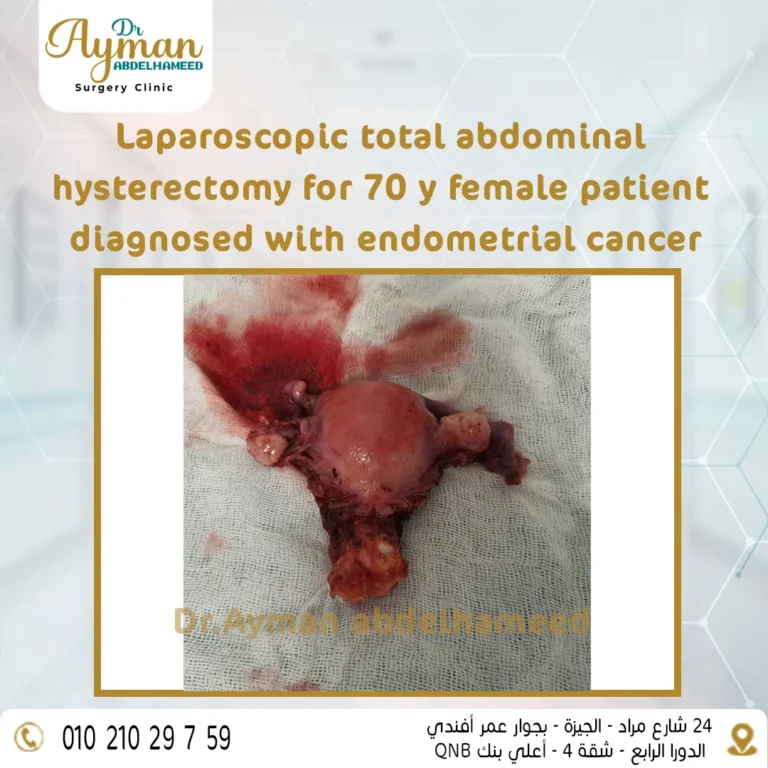
Endometrial cancer is treated with surgical intervention to remove the uterus and ovaries ، in addition to removing the fallopian tubes, ovaries and pelvic lymph nodes.
Here comes the role of minimally invasive surgery using advanced laparoscopy in removing the uterus without the traditional surgical incision. Through small holes in the abdominal wall.
It has several advantages, including: The amount of blood loss during surgery is less and there is less pain , compared to conventional surgery . In addition, the chances of surgical complications are less and less need for analgesics, thus helping patients return to their normal lives faster .
The patient does not need a long stay in the hospital, so he can be discharged from the hospital one day after the surgery in most cases, with nice small scars.
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are sometimes recommended after surgery if there is a risk of recurrence based on pathological analysis.
The role of periodic follow-up comes with detection and rumors every 3 to 6 months for the first two years and then every 6 to 12 months thereafter based on international scientific guidelines to complete the treatment plan.