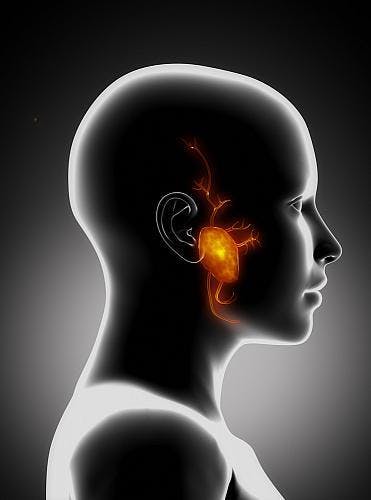
The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands and includes two lobes (superficial and deep)..
There are many reasons for the enlargement of the parotid gland, including inflammation, immune disease , or tumour Most of the parotid gland tumors of the benign type..
Cancer cells grow uncontrollably due to mutations in their DNA, . These cells may accumulate and form a tumor. Over time, cancer cells can grow to extend into normal tissues adjacent to the parotid gland or to the neck lymph nodes..
risk factors for developing a parotid tumor the following :
- Old age.
- Asbestos exposure.
- Radiation therapy for previous tumors in the head and neck region.
- Smoking
To diagnose a tumor in the parotid gland:
- Clinical examination of the neck
- US neck
- FNAC
- CT neck
- MRI neck
Parotid gland surgery represents the ideal solution for treatment, whether the surgery is to excise the superficial lobe of the gland or to remove the entire gland while preserving the facial nerve.
In case of malignant tumor, , the role of periodic follow-up comes with clinical examination of the neck and imaging such as ultrasound, CT scan or resonance on the neck every 6 months for the first two years and then every 12 months after that , based on international scientific guidelines to complete the treatment plan .