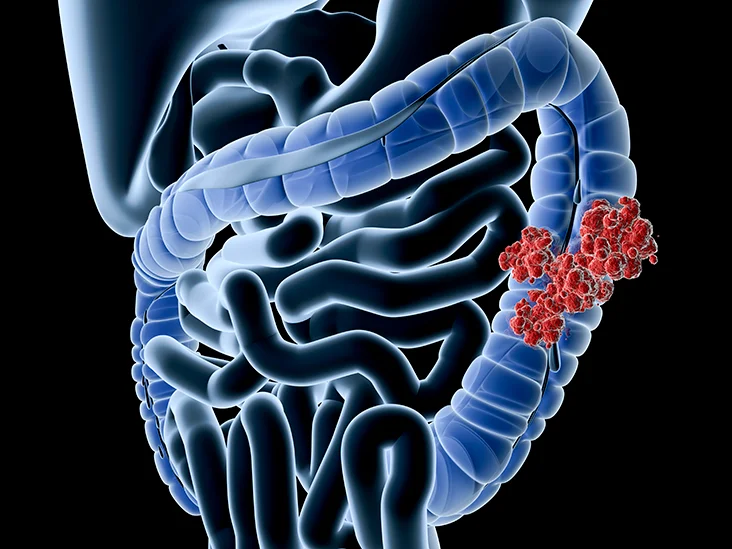
Colonic tumors are divided into benign and malignant. The colon is the final part of the digestive system . Despite the great similarity between colorectal cancer, the method of treating them is different . This is mainly due to the fact that the colon is anatomically different from the rectum.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!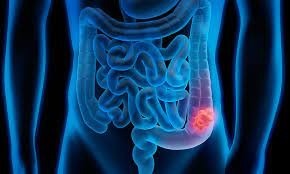
Colon cancer most commonly affects older adults, although it appears at any age. It usually begins as small, non-cancerous (benign) clumps of cells that are polyps that form inside the colon. Over time, some of these polyps may become colon cancer..
colon cancer manifestations include:
- Change in the nature of defecation, such as constipation and then diarrhea or vice versa.
- Blood in stool.
- Gas or pain in the pelvis, abdomen or back.
- Absence of a feeling of emptying the bowel after a bath.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Anemia..
Colon cancer does not manifest itself early in most cases, and signs vary according to the size and location of the tumor..
Cells in the colon wall grow uncontrollably, due to DNA mutations. These cells may accumulate and form a tumor. Over time, cancer cells can grow to extend into nearby normal tissues
In some families, colon cancer runs in families. There are two genetic syndromes that can be diagnosed with tests: Familial adenomatous polyposi (FAP). It is a rare disease that causes thousands of polyps in the lining of the rectum. The risk of developing colon or rectal cancer before the age of 40y increases. Lynch syndrome (LYNCH) increases the risk of colon cancer and other cancers such as uterine and breast cancer. People with Lynch syndrome tend to develop colorectal cancer before age 50 y.
Colon cancer risk factors include:
- Old age
- Personal history of colorectal cancer.
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn ‘s disease
- FAP syndrome
- LYNCH syndrome _
- smoking.
- unhealthy diet that contains little vegetables or red meat in excess
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity
- Uncontrolled DM
- exposure to radiation.
To reduce your risk of colon cancer ، do the following:
- Colorectal screening begins around age 45 y , or earlier if they have risk factors for colorectal cancer.
- lifestyle modifcation by exercising regularly.
- Change your diet to a healthy one. Contains fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Maintaining average weight.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
To confirm the diagnosis:
- Colonoscopy and biopsy.
- CT
- MRI
- CEA as a tumor marker
The treatment of colon cancer is different from the rectum as the role of surgery in colon cancer is upfront , even if the tumor size is large extending to other parts of the abdomen, such as the abdominal wall, ureter or urinary bladder.
Here comes the role of minimally invasive surgery using advanced laparoscopy in colon resection without the traditional surgical large incision through small holes in the abdominal wall.
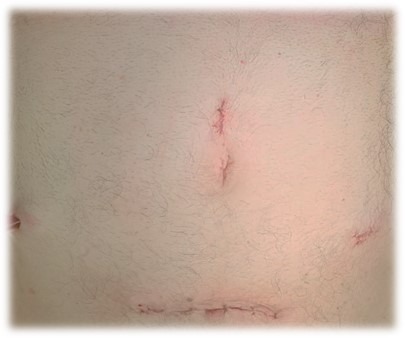
It has several advantages, including: The amount of blood loss during surgery is less and there is less pain , compared to conventional surgery . In addition, the chances of surgical complications are less and less need for analgesics and blood transfusions after surgery، thus helping patients return to their normal lives faster compared to other surgeries.
The patient does not need a long stay in the hospital, so he can be discharged from the hospital a few days after the surgery. without the need to special wound care.
Adjuvant treatment is determined after the analysis of the tumor and lymph nodes to define the accurate stage.
The role of periodic follow-up comes with clinical examination CT and colonoscopy every 3 to 6 months for the first two years and then every 6 to 12 months thereafter based on international scientific guidelines to complete the treatment plan..